Consider a graph
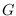
and a real-valued function
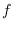
defined on the
degree set of
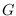
. The sum of the outputs
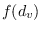
over all vertices
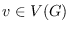
of
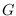
is usually known as the vertex-degree-function
index and is denoted by
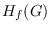
, where
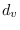
represents the degree
of a vertex
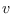
of
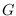
. This paper gives sharp bounds on the index
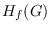
in terms of order and size of
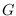
when
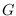
is connected and
has the maximum degree at most
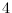
. All the graphs achieving the
derived bounds are also determined. Bounds involving several
existing indices - including the general zeroth-order Randic
index and coindex, the general multiplicative first/second Zagreb
index, the variable sum lodeg index, the variable sum exdeg index -
are deduced as the special cases of the obtained ones.