We consider a simple graph
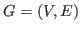
without isolated vertices and of minimum degree
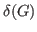
.
Let
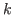
be an integer number such that
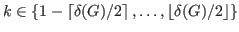
.
A vertex
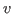
of
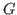
is said to be
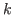
-controlled by a set
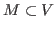
, if
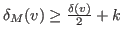
where
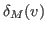
represents the number of neighbors
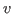
has in
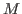
and
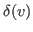
the degree
of
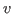
. The set
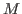
is called a
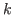
-monopoly if it
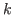
-controls every vertex
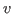
of
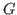
. The minimum cardinality of any
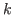
-monopoly in
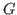
is the
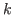
-monopoly number of
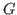
. In this article we study the
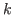
-monopolies of
the lexicographic product of graphs. Specifically we obtain several
relationships between the
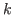
-monopoly number of this product graph and the
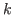
-monopoly numbers and/or order of its factors. Moreover, we bound (or
compute the exact value) of the
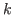
-monopoly number of several families of
lexicographic product graphs.